Introduction
Did you know that an engine and its components did not function without a starter motor? Have you ever analyzed the process by which a starter motor works?
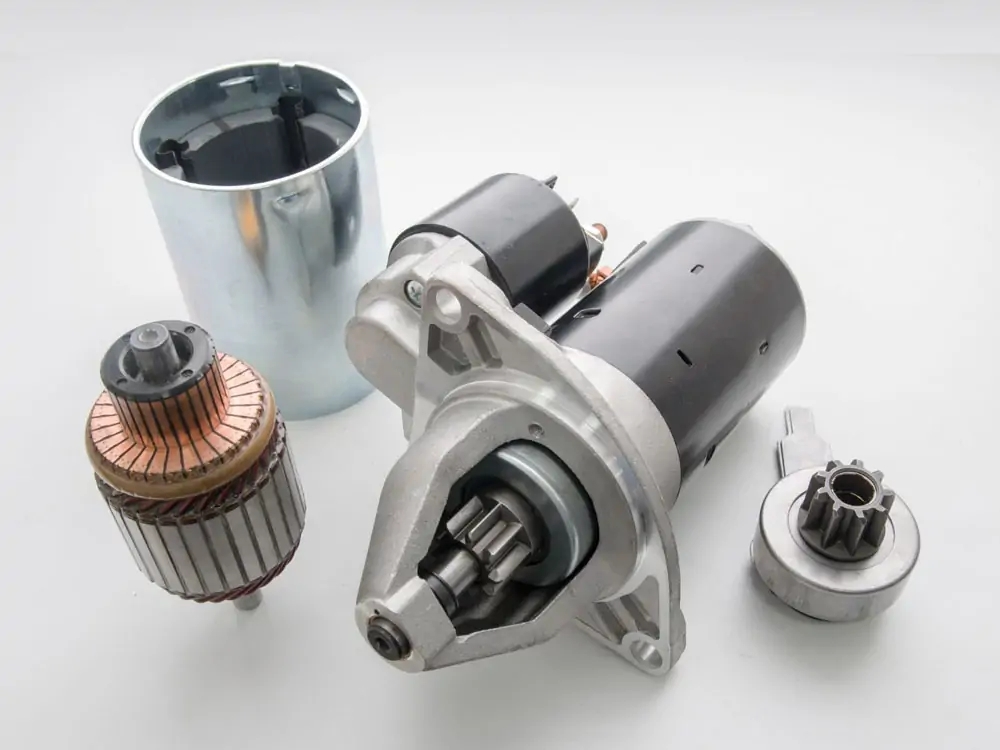

As you should know, this often overlooked part is significant for engine starters. One of the most vital parts is the starter motor components of an inside ignition engine. It enables the engine to start. This component of your vehicle starts the engine by initially turning the crankshaft.
This article focuses primarily on the definition, how the starter motor works, construction, where it is located, function, parts, types, and adverse symptoms of engine starters.
What Is a Starter Motor?
A mechanical device known as a starter motor is used in internal combustion engines (ICEs) to spin the engine’s crankshaft. It makes getting the engine’s primary operation feasible using the internal power it generates.
A vital part of an engine’s functioning is the starter, also known as a starter motor, engine starter, or cracking motor. These motors are operated using pneumatic, electrical, or hydraulic motors.
How Starter Motor Works?
The way works the starter motor is precise. Inside the structure, there are 4 field-windings. Carbon connects the frame to the loops. The battery in the car runs the engine starter. The battery is on and transforms power to the solenoid when you turn the ignition key.
The engine starts receiving power from the solenoid once again. The starter must first involve the pinion gears to engage the flywheel of engine. The flywheel attaches to the crank of the engine.
The flywheel turns with the motor, which turns the crankshaft even more. The engine starts when the crank-shaft rotates, and the mixture of air and fuel begins to ignite. When the mixture of air and fuel begins combustion, the motor intercepts. The engine starter gets more power from the combustion of the mixture.
Where Is the Starter Located in the Car?
Do you know where the starter is to be found? There are three main locations. It lies beneath the manifold and above the transmission on the driver’s side. It is also located under the exhaust manifold on the passenger’s side.
Different vehicles have different starter positions. According to the vehicle’s layout, the starter is located on the passenger or driver’s side.
The starter for front-wheel drive (FWD) is located beneath the left bank of the cylinders on the driver’s side of the engine. In a car with rear-wheel drive (RWD), the engine starter is located near the transmission on the passenger’s side of the engine’s bottom part. Bolts act for fixing and securing the part to the mounting plate. Additionally, two wires linked to the starter.
How Starter Motor Constructs?
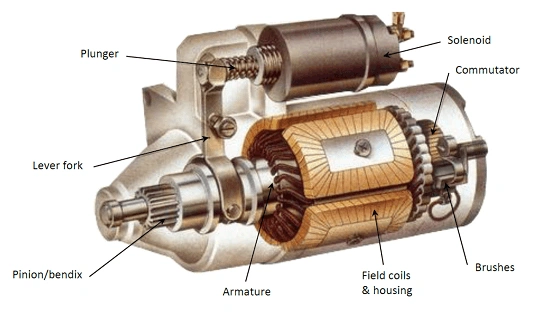
The generator and the engine starter are both built the same way. However, the brush terminals are heavier to handle high currents. Copper or another low-resistance metal is used for the brushes instead of carbon, which is used for the generator case.
The commutator, casing, armature, poles, field winding brushes, and terminals are the major components of the engine starter. The motor starts the engine with the help of a drive mechanism at the end of the armature shaft.
To start, the motor has either two or four field windings. When the current from the battery flows into the motors, it divides into branches, each branch reaching a different field winding. Current flows from the fields to the armature’s commutator and passes through the two insulated brushes. The current in the armature makes four poles afterwards to the four field poles simultaneously.
These form the attractive and repulsive forces that turn the armature. Through the two grounded brushes, the current in the armature goes back to the battery. Many massive engines use it to make more power.
What Are the Parts of the Starter Motor?
Engine starter consists of the subsequent components:
- Brushes and Commutator
- Armature
- Lever Fork
- Field Coils
- Solenoid
- Plunger or Piston
- Pinion
Let’s explain each type of starter motor or engine starter in detail.
- Commutator and Brushes
The back of the engine starting housing is where you’ll find the commutator. The structure consists of 2 plates securely attached to the axis of the armature-shaft. The carbon brushes establish a vital electrical link between every plate, facilitating the necessary power link for the windings of the armature.
- Armature
This component constitutes an integral element of the engine starter. The installation is carried out upon the driveshaft or bearing to act as a directing mechanism. The armature is comprised of a core made of soft iron. The core is covered by a series of loops or windings consisting of multiple electrical conductors.
- Lever Fork
The lever fork is securely affixed on the one end of the plunger. Upon the plunger’s moves into the solenoid core, the lever fork continually exerts power, thus causing the pinion-gear to extend outward and establish a seamless interconnected connection with the flywheel ring gear.
- Field Coils
The field coils are securely attached within the casing using screws, comprising multiple interconnected coils in a series form. These coils are powered by the battery, which effectively transforms power into a magnetic field, which helps the rotation of the armature. The armature’s structure induces a magnetic field’s formation in its surroundings.
- Solenoid
A starter solenoid is also a strong electric switch. A standard starter solenoid has two larger terminals with an input for the positive battery cable, an output for the cable that powers the starter motor, and a small connector for the wire connecting to the starting key. Typically, the solenoid contains two wire coils around a plunger.
The coils do two functions:
- A strong coil that closes forces in the plunger
- A weaker coil that holds the plunger in position. This draws power away from the strong coil, which saves some power.
The control circuit sets off the solenoid, which also moves the pinion gear to line up with the spinning ring gear. It closes the starter circuit and transfers energy from the battery to the engine starter.
- Piston or Plunger
Its installation occurs at the pinion’s terminal. It moves while connecting the pinion.
- Pinion
A pinion is a gear and spring-containing small mechanism. It contacts the flywheel teeth by extending the gear right when the engine starts. The flywheel provides rotary motion to the engine.

What Are the Types of Starter Motors?
The following are the main kinds:
- Planetary Gear-Reduction Starter (PLGR)
- Off-Set Gear Reduction (OSGR)
- Inertial Starter
- Permanent Magnet Gear Reduction (PMGR)
- Permanent Magnet Direct-Drive Reduction
- Direct Drive (DD) Starter Motor
- Planetary Gear Reduction Starter (PLGR)
Planetary gear reduction starter has substantially displaced direct-drive starters. A permanent-magnet facilitates power transfer from the armature to the pinion-shaft. This gear’s armature rotates at a quicker rate. The primary purpose of planetary gear is to decrease gear, diminishing the need for a high current.
A sun gear is located at the end of the armature, while the stationary ring gear contains three plenary carrier gears. Great gear reductions are possible with planetary gears because the ring gear retains the sun gear and outputs the carrier’s power.
- Off-Set Gear Reduction (OSGR)
This kind of engine starter or starter motor operates at high speeds while consuming low currents. Off-set gear reduction generators are lightweight, compact, and simple to assemble. Due to their increased operating torque, off-set gear reduction starters are prevalent in four-wheel-drive vehicles. Because they increase initiating torque, they are most frequently installed on 4WD vehicles.
Advantages:
- More powerful
- Suitable for larger engines and harsher environments
- Longer lifespan
- Direct-Drive Starter Motor (DD)
It is among the earliest and most well-known varieties of starters offered. The way it works with direct drives is comparable to that of other varieties. It works via solenoid devices. A wide variety of direct-drive starter designs are accessible to consumers. A direct connection exists between the solenoid and the automobile power battery. Compressing the ignition button supplies power to the solenoid via the vehicle’s battery.
When current flows through the solenoid, it pulls both the lever and plunger, which in turn helps the pinion rotate. The combustion engine’s flywheel is subsequently connected to the pinion. As the starter motor rotates, the spinning flywheel spins, causing combustion to start in the engine’s combustion chamber.
Advantages:
- Affordable
- Efficient design
- Low maintenance
- Inertial Starter
Inertial starters refer to electric starters that can cover all starter motors. It works effectively during the cranking phase and effectively protects the motor component. The engine has a robust and rapid start, making it the optimal choice for achieving excellent speed. The weight attributed to the twisting capability of the entire starter has been substantially decreased.
- Permanent Magnet Gear Reduction
Another important type of engine starter is permanent magnet gear reduction. The permanent magnet gear reduction will make the device simple to build, lighter in weight, and produce less heat. It contains four or six magnet field assemblies in place of field coil openers. There are three connections on the 12V solenoid. It’s heavy-duty, so it needs less power. It has no field coils, so the current goes straight from the brushes and commutator to the armature.
- Permanent Magnet Direct-Drive (PMDD)
In numerous aspects, PMDD starter motor varieties resemble direct drive motors. The field coil is substituted with permanent magnets in the permanent magnet direct drive type.
What Are the Sings Indicate a Faulty Starter Motor?
If your engine starter is malfunctioning, you may notice any of the following signs:
- Clicking noise or Whirring
- Hard to start the engine
- Smoking and overheating
- Engine not start
- The dashboard illuminates up. However, the engine does not start
Starter Motor Replacement Cost
The cost to replace an engine starter can differ based on factors such as the brand, model of your vehicle, and labor cost. The replacement cost for the engine starter typically ranges between $200 to $1200. The labor cost ranges from $140 to $1,000.
Conclusion
After reading this, you should have an enhanced understanding of how the starter motor works and how it is vital for your vehicle engine. Regular maintenance can keep your car operating smoothly and effectively, preventing problems. For optimum performance, it’s important to monitor for alert signs that indicate the engine starter needs maintenance.
